Overview[]
The Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program (FedRAMP) is a unified, government-wide risk management program focused on large outsourced and multi-agency systems. FedRAMP has been established to provide a standard approach to Assessing and Authorizing (A&A) cloud computing services and products. FedRAMP allows joint authorizations and continuous security monitoring services for Government and Commercial cloud computing systems intended for multi-agency use.
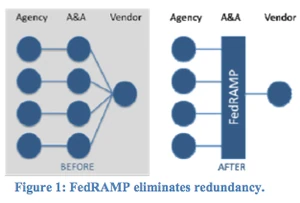
FedRAMP was established on December 8, 2011, via an official memorandum from the Federal Chief Information Officer to all Federal CIOs. FedRAMP reached initial operational capabilities in June 2012. According to OMB, FedRAMP will reduce duplicative efforts, inconsistencies, and cost inefficiencies associated with the current security authorization process. This approach uses a "do once, use many times" framework that will save costs, time, and staff required to conduct redundant agency security assessments.
Participants[]
There are five major participants in the FedRAMP process:
- Federal agency customer: any Federal agency that has a requirement for cloud technology.
- Cloud service provider: a private (e.g., Amazon, Microsoft, IBM, etc.) or public (e.g., a Federal agency offering services to other federal agencies) entity willing and able to fulfill customer requirements.
- Joint Authorization Board: a panel composed of representatives from GSA and the Departments of Defense and Homeland Security that reviews the security package submitted by the cloud service provider and grants the service provider provisional authority to operate.
- Third party assessor: an entity such as a public accounting firm that validates the quality and compliance of the cloud service provider's security program.
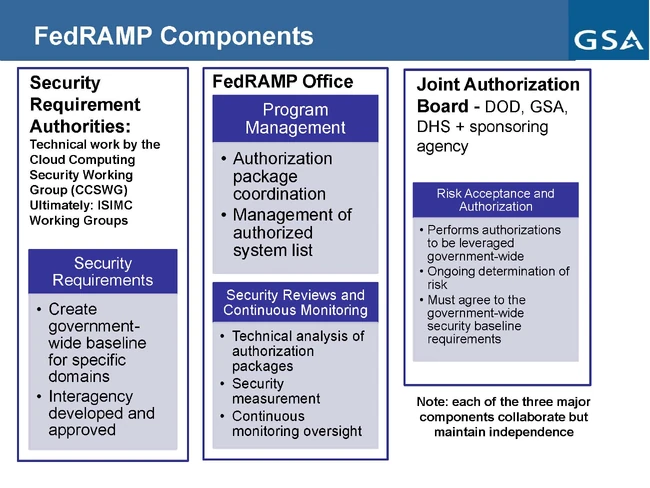
- FedRAMP Program Management Office: a GSA group that provides operational management of the FedRAMP process and ensures effective communication among all stakeholders.
Objective[]
The objective of FedRAMP is threefold:
- Ensure that information systems/services used government-wide have adequate information security;
- Eliminate duplication of effort and reduce risk management costs; and
- Enable rapid and cost-effective procurement of information systems/services for federal agencies.
Joint authorization of cloud providers results in a common security risk model that can be leveraged across the U.S. federal government. The use of this common security risk model provides a consistent baseline for cloud- based technologies. This common baseline ensures that the benefits of cloud-based technologies are effectively integrated across the various cloud computing solutions currently proposed within the government. The risk model will also enable the government to "approve once, and use often" by ensuring multiple agencies gain the benefit and insight of the FedRAMP's Authorization and access to service provider’s authorization packages.
Such a program will promote the goals of openness and transparency in government. All of the security requirements, processes, and templates will have to be made publicly available for consumption not only by Federal agencies but private vendors as well. This will allow Federal Agencies to leverage this work at their agency but private industry will also finally have the full picture of what a security authorization will entail prior to being in a contractual relationship with an agency.
FedRAMP provides security authorizations and continuous monitoring of shared systems that can be leveraged by agencies to both reduce their security compliance burden and provide them highly effective security services.
FedRAMP will establish a unified risk management process by:
- Creating agreed-upon security requirements among federal departments and agencies.
- Ensuring compatible security requirements on shared systems.
- Eliminating duplication of effort and associated cost savings.
- Enabling rapid acquisition by leveraging pre-authorized solutions.
- Encouraging better system integration with government-wide information security efforts.
- Increasing security through focus assessments.
Governance[]
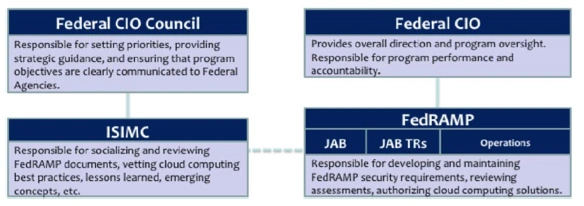
FedRAMP is an interagency effort under the authority of the U.S. Chief Information Officer (U.S. CIO) and managed out of the General Services Administration (GSA) as depicted in Figure 3.
Figure 3. FedRAMP Governance Model.
The initiation of FedRAMP and the Joint Authorization Board (JAB) has been via the U.S. CIO in coordination with the Federal CIO Council. The U.S. CIO has tasked the JAB with jointly authorizing cloud computing systems. The General Services Administration (GSA) has been tasked with the actual day-to-day operation of FedRAMP in supports this effort.
The three permanent members of JAB include the Department of Homeland Security (DHS), Department of Defense (DOD), and the GSA. The sponsoring government agency for each cloud computing system will be represented as the rotating JAB member. The JAB also performs risk determination and acceptance of FedRAMP authorized systems.
The JAB also has the final decision making authority on FedRAMP security controls, policies, procedures and templates.
JAB technical representatives are appointed by their respective JAB authorizing official (both permanent and rotating) for the implementation of the FedRAMP process. JAB technical representatives provide subject matter expertise and advice to the JAB authorizing officials.
The JAB technical representatives review the vetted authorization packages provided by FedRAMP. The JAB technical representatives make authorization recommendations to the JAB authorizing officials and advise the JAB of all residual risks.
FedRAMP is an administrative support team provided by the U.S. CIO under the guidance of GSA. FedRAMP operations are responsible for the day-to-day administration and project management of FedRAMP. FedRAMP performs an initial review of submitted authorization packages and has the authority to work with cloud computing system owners to refine each submission until it satisfies FedRAMP and JAB requirements. FedRAMP also oversees continuous monitoring of authorized systems.
The ISIMC under the Federal CIO Council is responsible for socializing and reviewing FedRAMP processes and documents. They provide recommendations on the FedRAMP documents directly to the JAB. Their recommendations are based on vetting the cloud computing best practices, lessons learned and emerging concepts within the Federal CIO Council community. However, the final approval on changes to FedRAMP processes and documents is made by the JAB.
Role of NIST[]
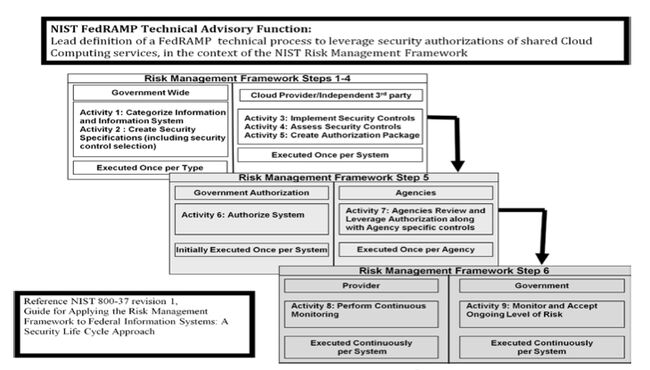
NIST, in the technical advisory role to the interagency Federal Cloud Computing Advisory Council (CCAC) Security Working Group will define an initial technical approach and process for FedRAMP consistent with NIST security guidance in the context of the Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA). To clarify the role of NIST with respect to FedRAMP, while NIST is supporting the definition of the FedRAMP process from a technical perspective, NIST is not the implementing organization. The governance and operational implementation of FedRAMP will be completed under the auspices of the Federal CIO Council.
As part of its technical advisory effort, NIST will:
- Provide technical support and leadership to the working groups supporting the Federal CIO Council.
- Create guidance to facilitate leveraged Government authorization of cloud systems and on the application of FISMA and NIST Special Publication 800-53 to cloud computing.
Source[]
- "Participants" section: NASA's Progress in Adopting Cloud-Computing Technologies, at 8.