Definition[]
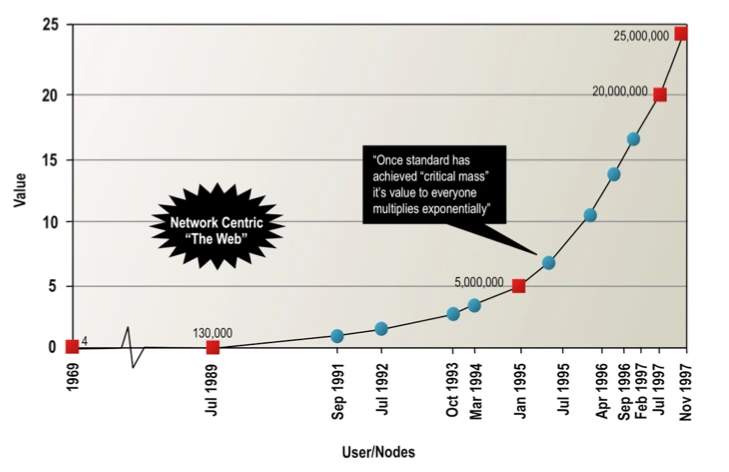
Metcalfe's Law says that the value of a network is equivalent to the square of the number of connected users of the system.[1] In other words, as networks grow, the utility of being connected to the network not only grows, but does so exponentially. Thus when a person is added to the network, all network members are affected.
Overview[]
As the bandwidth available through the network continues to grow, Metcalfe's Law dictates that the value of a connection increases exponentially. The ratio of the cost of Internet access to the value it provides plummets over time. And as it plummets, connectivity and higher-bandwidth connections become that much more important, generating more usage and more capital to upgrade the network.