No edit summary |
|||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
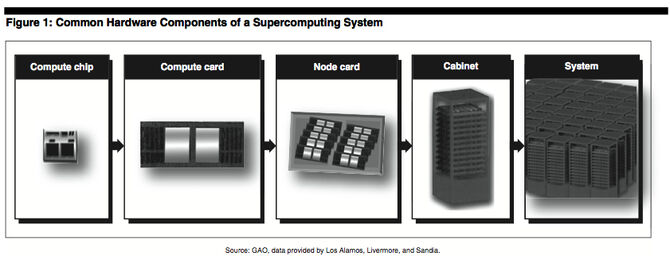
Figure 1 shows the common components of a supercomputing system. |
Figure 1 shows the common components of a supercomputing system. |
||
| − | [[File:Supercomputer.jpg|left| |
+ | [[File:Supercomputer.jpg|left|670px]] |
[[Category:Computing]] |
[[Category:Computing]] |
||
[[Category:Hardware]] |
[[Category:Hardware]] |
||
Revision as of 00:19, 10 December 2010
Definition
Supercomputing systems employ a large number of interdependent processors, which are the core unit of a computer that gathers instructions and data. These processors are mounted onto a compute chip, which is the portion of the system that carries out the instructions of a computer program. These compute chips are inserted onto a compute card, which also holds memory for the compute chips to use. A number of compute cards are attached to a node card, which have one or more processors with a common memory and are connected by high-speed interconnection networks. Each node card is inserted into a single cabinet, and that configuration is repeated many times to build a single supercomputing system.
Each supercomputing system has a peak performance, which is the maximum rate of floating-point operations per second (FLOPS) that the system can sustain.
Figure 1 shows the common components of a supercomputing system.