No edit summary |
m (→Security) Tag: Source edit |
||
| (45 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | == Definitions == |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| + | |||
| + | === Biometrics === |
||
| + | |||
| + | A '''threat''' is |
||
| + | |||
| + | {{Quote|[a]n [[intentional]] or [[unintentional]] potential event that could [[compromise]] the [[security]] and [[integrity]] of the [[system]].<ref>[[NSTC Subcommittee on Biometrics]], Biometrics Glossary, at 27 (Sept. 14, 2006) ([http://www.biometrics.gov/Documents/Glossary.pdf full-text]).</ref>}} |
||
| + | |||
| + | === General === |
||
| + | |||
| + | A '''threat''' is |
||
| + | |||
| + | {{Quote|[t]he capability of an [[adversary]] coupled with his/her [[intention]]s to undertake any actions detrimental to the success of program activities or operations.<ref>[[DOE Manual 470.4-7]], at 60.</ref>}} |
||
| + | {{Quote|[a] natural or man-made occurrence, individual, entity, or action that has or indicates the potential to harm life, [[information]], operations, the environment, and/or property.<ref>[[DHS Risk Lexicon]], at 36.</ref>}} |
||
| + | {{Quote|[a] potential cause of an unwanted [[incident]], which may result in harm to a [[system]] or organization.<ref>[[ISO/IEC 27000:2014]].</ref>}} |
||
| + | |||
| + | === Medical device === |
||
| + | |||
| + | A '''threat''' is |
||
| + | |||
| + | {{Quote|any circumstance or event with the potential to adversely impact the [[essential clinical performance]] of the [[device]], organizational operations (including mission, functions, [[image]], or [[reputation]]), organizational assets, individuals, or other organizations through an [[information system]] via [[unauthorized access]], [[destruction]], [[disclosure]], [[modification]] of [[information]], and/or [[denial of service]]. Threats exercise [[vulnerabilities]], which may impact the [[essential clinical performance]] of the [[device]].<ref>[[Postmarket Management of Cybersecurity in Medical Devices: Draft Guidance for Industry and Food and Drug Administration Staff]], at 9-10.</ref>}} |
||
| + | |||
| + | === Security === |
||
| + | |||
| + | A '''threat''' is |
||
| + | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| + | {{Quote|any circumstance or event with the potential to [[intentional]]ly or [[unintentional]]ly [[exploit]] one or more [[vulnerabilities]] in a [[system]] resulting in a loss of [[confidentiality]], [[integrity]], or [[availability]].<ref>[[Federal Plan for Cyber Security and Information Assurance Research and Development]], at 5.</ref>}} |
||
| + | {{Quote|[a] potential cause of an [[incident]], that may result in harm of [[system]]s and organization.<ref>[[ISO/IEC 27005:2011]].</ref>}} |
||
| + | {{Quote|a potential undesirable event, [[malicious]] or not, of (1) [[compromise]] (i.e., [[theft]] of valuable or [[sensitive information]] or services), (2) [[corruption of information]] or [[information service]]s, or (3) [[denial of service]] by [[degradation]]/[[blocking]] of [[data]], [[data processing|processing]], or [[communication]]s or an entity possessing the capability and [[intent]] to cause the above.<ref>[[Report on the NS/EP Implications of Intrusion Detection Technology Research and Development]], at 6 n.7.</ref>}} |
||
| + | {{Quote|[a]ny circumstance or event with the potential to adversely impact agency operations (including mission, functions, image, or [[reputation]]), agency [[asset]]s, or individuals through an [[information system]] via [[unauthorized access]], [[destruction]], [[disclosure]], [[modification]] of [[information]], and/or [[denial of service]].<ref>[[NIST Special Publication 800-82]], at B-8.</ref>}} |
||
| + | {{Quote|[a]ny circumstance or event with the potential to adversely impact organizational operations, organizational assets, individuals, other organizations, or the Nation through a [[system]] via [[unauthorized access]], [[destruction]], [[disclosure]], [[modification]] of [[information]], and/or [[denial of service]].<ref>[[NIST Special Publication 800-171B]], App. B, at 51.</ref>}} |
||
| + | |||
| + | == Overview == |
||
| + | |||
| + | Threats are implemented by [[threat agent]]s. |
||
[[File:Snapshot_2009-11-07_20-17-23.jpg]] |
[[File:Snapshot_2009-11-07_20-17-23.jpg]] |
||
| + | == Information systems == |
||
| ⚫ | [[Information system]]s are subject to serious |
||
| ⚫ | [[Information system]]s are subject to serious threats that can have adverse effects on organizational operations (including missions, functions, image, or [[reputation]]), organizational [[asset]]s, individuals, other organizations, and the government by [[compromising]] the [[confidentiality]], [[integrity]], or [[availability]] of [[information]] being [[data processing|processed]], [[store]]d, or [[transmit]]ted by those [[system]]s. |
||
| ⚫ | Threats to [[information system]]s include environmental disruptions, human errors, and purposeful [[attack]]s. [[Attack]]s on [[information system]]s today are often well-organized, disciplined, aggressive, well-funded, and in a growing number of documented cases, extremely sophisticated. Successful [[attack]]s on public and private sector information |
||
| + | |||
| ⚫ | Threats to [[information system]]s include environmental disruptions, human errors, and purposeful [[attack]]s. [[Attack]]s on [[information system]]s today are often well-organized, disciplined, aggressive, well-funded, and in a growing number of documented cases, extremely sophisticated. Successful [[attack]]s on public and private sector [[information system]]s can result in great harm to the [[national security|national]] and economic security interests of a country. |
||
| + | |||
| + | Indeed, [[system]]s sometimes fail without any external provocation, as a result of [[design flaw]]s, [[implementation]] [[bug]]s, [[misconfiguration]], and [[system]] aging. |
||
| + | |||
| + | Additional threats arise in the [[system acquisition]] and [[code distribution]] processes. Serious [[security]] problems have also resulted from discarded or stolen [[system]]s. For large-scale systems consisting of many independent [[installation]]s (such as the [[Domain Name System]] ([[DNS]])), [[security update]]s must reach and be [[install]]ed in all relevant [[component]]s throughout the entire [[life cycle]] of the [[system]]s. This scope of [[updating]] has proven to be difficult to achieve. |
||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:IWThreat.jpg]] |
||
| + | |||
| + | == References == |
||
| + | <references /> |
||
== See also == |
== See also == |
||
| + | <div style="{{column-count|4}}"> |
||
| + | |||
| + | * [[Adaptive threat]] |
||
| + | * [[Cyber threat]] |
||
| + | * [[Cybersecurity threat ]] |
||
| + | * [[Environmental threat]] |
||
* [[External threat]] |
* [[External threat]] |
||
| + | * [[Hazard]] |
||
| + | * [[Human threat]] |
||
| + | * [[Hybrid threat]] |
||
* [[Insider threat]] |
* [[Insider threat]] |
||
| + | * [[Intentional threat]] |
||
* [[Internal threat]] |
* [[Internal threat]] |
||
| + | * [[IO threat]] |
||
| + | * [[Local threat]] |
||
| + | * [[National security threat]] |
||
| + | * [[Outside threat]] |
||
| + | * [[Outsider threat]] |
||
| + | * [[Physical threat]] |
||
| + | * [[Security threat]] |
||
| + | * [[Shared threat]] |
||
| + | * [[Supply system threat]] |
||
| + | * [[Threat action]] |
||
| + | * [[Threat analysis]] |
||
| + | * [[Threat and Vulnerability Testing and Assessment]] |
||
| + | * [[Threat assessment]] |
||
| + | * [[Threat band]] |
||
| + | * [[Threat condition]] |
||
| + | * [[Threat focus cell]] |
||
| + | * [[Threat inventory]] |
||
| + | * [[Threat model]] |
||
| + | * [[Threat monitoring]] |
||
| + | * [[Threat signaling]] |
||
| + | * [[Unintentional threat]] |
||
| + | * [[Vulnerability]] |
||
[[Category:Security]] |
[[Category:Security]] |
||
| + | [[Category:Cybercrime]] |
||
[[Category:Computer crime]] |
[[Category:Computer crime]] |
||
| + | [[Category:Definition]] |
||
Latest revision as of 11:45, 16 November 2020
Definitions[]
Biometrics[]
A threat is
| “ | [a]n intentional or unintentional potential event that could compromise the security and integrity of the system.[1] | ” |
General[]
A threat is
| “ | [t]he capability of an adversary coupled with his/her intentions to undertake any actions detrimental to the success of program activities or operations.[2] | ” |
| “ | [a] natural or man-made occurrence, individual, entity, or action that has or indicates the potential to harm life, information, operations, the environment, and/or property.[3] | ” |
| “ | [a] potential cause of an unwanted incident, which may result in harm to a system or organization.[4] | ” |
Medical device[]
A threat is
| “ | any circumstance or event with the potential to adversely impact the essential clinical performance of the device, organizational operations (including mission, functions, image, or reputation), organizational assets, individuals, or other organizations through an information system via unauthorized access, destruction, disclosure, modification of information, and/or denial of service. Threats exercise vulnerabilities, which may impact the essential clinical performance of the device.[5] | ” |
Security[]
A threat is
| “ | any circumstance or event with the potential to cause harm to a system in the form of destruction, disclosure, modification of data, and/or denial of service.[6] | ” |
| “ | any circumstance or event with the potential to intentionally or unintentionally exploit one or more vulnerabilities in a system resulting in a loss of confidentiality, integrity, or availability.[7] | ” |
| “ | [a] potential cause of an incident, that may result in harm of systems and organization.[8] | ” |
| “ | a potential undesirable event, malicious or not, of (1) compromise (i.e., theft of valuable or sensitive information or services), (2) corruption of information or information services, or (3) denial of service by degradation/blocking of data, processing, or communications or an entity possessing the capability and intent to cause the above.[9] | ” |
| “ | [a]ny circumstance or event with the potential to adversely impact agency operations (including mission, functions, image, or reputation), agency assets, or individuals through an information system via unauthorized access, destruction, disclosure, modification of information, and/or denial of service.[10] | ” |
| “ | [a]ny circumstance or event with the potential to adversely impact organizational operations, organizational assets, individuals, other organizations, or the Nation through a system via unauthorized access, destruction, disclosure, modification of information, and/or denial of service.[11] | ” |
Overview[]
Threats are implemented by threat agents.
Information systems[]
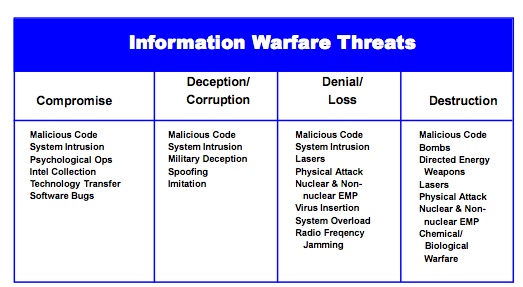
Information systems are subject to serious threats that can have adverse effects on organizational operations (including missions, functions, image, or reputation), organizational assets, individuals, other organizations, and the government by compromising the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of information being processed, stored, or transmitted by those systems.
Threats to information systems include environmental disruptions, human errors, and purposeful attacks. Attacks on information systems today are often well-organized, disciplined, aggressive, well-funded, and in a growing number of documented cases, extremely sophisticated. Successful attacks on public and private sector information systems can result in great harm to the national and economic security interests of a country.
Indeed, systems sometimes fail without any external provocation, as a result of design flaws, implementation bugs, misconfiguration, and system aging.
Additional threats arise in the system acquisition and code distribution processes. Serious security problems have also resulted from discarded or stolen systems. For large-scale systems consisting of many independent installations (such as the Domain Name System (DNS)), security updates must reach and be installed in all relevant components throughout the entire life cycle of the systems. This scope of updating has proven to be difficult to achieve.
References[]
- ↑ NSTC Subcommittee on Biometrics, Biometrics Glossary, at 27 (Sept. 14, 2006) (full-text).
- ↑ DOE Manual 470.4-7, at 60.
- ↑ DHS Risk Lexicon, at 36.
- ↑ ISO/IEC 27000:2014.
- ↑ Postmarket Management of Cybersecurity in Medical Devices: Draft Guidance for Industry and Food and Drug Administration Staff, at 9-10.
- ↑ National Cyber Incident Response Plan, at M-1.
- ↑ Federal Plan for Cyber Security and Information Assurance Research and Development, at 5.
- ↑ ISO/IEC 27005:2011.
- ↑ Report on the NS/EP Implications of Intrusion Detection Technology Research and Development, at 6 n.7.
- ↑ NIST Special Publication 800-82, at B-8.
- ↑ NIST Special Publication 800-171B, App. B, at 51.
See also[]
- Adaptive threat
- Cyber threat
- Cybersecurity threat
- Environmental threat
- External threat
- Hazard
- Human threat
- Hybrid threat
- Insider threat
- Intentional threat
- Internal threat
- IO threat
- Local threat
- National security threat
- Outside threat
- Outsider threat
- Physical threat
- Security threat
- Shared threat
- Supply system threat
- Threat action
- Threat analysis
- Threat and Vulnerability Testing and Assessment
- Threat assessment
- Threat band
- Threat condition
- Threat focus cell
- Threat inventory
- Threat model
- Threat monitoring
- Threat signaling
- Unintentional threat
- Vulnerability